|
|
|
Pricing supplement
To prospectus dated April 8, 2020,
prospectus supplement dated April 8, 2020 and
product supplement no. 2-II dated November 4, 2020
|
Registration Statement Nos. 333-236659 and 333-236659-01
Dated July 1, 2022
Rule 424(b)(2)
|
| JPMorgan Chase Financial Company LLC |
Structured
Investments |
$950,000
Digital Contingent Buffered Notes Linked to a Brent Crude
Oil Futures Contract due July 31, 2023
Fully and Unconditionally Guaranteed by JPMorgan Chase
& Co. |
General
| · | The
notes are designed for investors who seek a fixed return of 16.00% if the Ending Contract Price of the Commodity Futures Contract is
greater than or equal to the Initial Contract Price or is less than the Initial Contract Price by up to 50%. |
| · | Investors
should be willing to forgo interest payments and be willing to lose some or all of their principal if the Ending Contract Price is less
than the Initial Contract Price by more than 50%. |
| · | The
notes are unsecured and unsubordinated obligations of JPMorgan Chase Financial Company LLC, which we refer to as JPMorgan Financial,
the payment on which is fully and unconditionally guaranteed by JPMorgan Chase & Co. Any payment on the notes is subject to the
credit risk of JPMorgan Financial, as issuer of the notes, and the credit risk of JPMorgan Chase & Co., as guarantor of the notes. |
| · | Minimum
denominations of $10,000 and integral multiples of $1,000 in excess thereof |
Key Terms
| Issuer: |
JPMorgan Chase Financial Company LLC, an indirect, wholly owned finance subsidiary of JPMorgan Chase & Co. |
| Guarantor: |
JPMorgan Chase & Co. |
| Commodity Futures Contract: |
The first nearby month futures contract for Brent crude oil (Bloomberg ticker: CO1) traded on ICE Futures Europe or, on any day that falls on the last trading day of such contract (all pursuant to the rules of ICE Futures Europe), the second nearby month futures contract for Brent crude oil (Bloomberg ticker: CO2) traded on ICE Futures Europe |
| Payment at Maturity: |
If the Ending Contract Price is greater than or equal to the Initial Contract Price or is less than the Initial Contract Price by up to the Contingent Buffer Percentage, at maturity you will receive a cash payment that provides you with a return per $1,000 principal amount note equal to the Contingent Digital Return. Accordingly, under these circumstances, your payment at maturity per $1,000 principal amount note will be calculated as follows: |
| $1,000 + ($1,000 × Contingent Digital Return) |
| If the Ending Contract Price is less than the Initial Contract Price by more than the Contingent Buffer Percentage, at maturity you will lose 1% of the principal amount of your notes for every 1% that the Ending Contract Price is less than the Initial Contract Price. Under these circumstances, your payment at maturity per $1,000 principal amount note will be calculated as follows: |
| |
$1,000 + ($1,000 × Contract Return)
In no event, however, will the payment at maturity be less than $0. |
| |
If the Ending Contract Price is less than the Initial Contract Price by more than the Contingent Buffer Percentage of 50%, you will lose more than 50% of your principal amount at maturity and may lose all of your principal amount at maturity. |
| Contingent Digital Return: |
16.00%, which reflects the maximum return on the notes. Accordingly, the maximum payment at maturity per $1,000 principal amount note is $1,160.00. |
| Contingent Buffer Percentage: |
50% |
| Contract Return: |
Ending Contract Price – Initial Contract Price
Initial Contract Price |
| Initial Contract Price: |
The Contract Price on the Pricing Date, which was $111.63 |
| Ending Contract Price: |
The Contract Price on the Observation Date |
| Contract Price: |
On any day, the official settlement price per barrel on ICE Futures Europe of the first nearby month futures contract for Brent crude oil, stated in U.S. dollars, provided that if that day falls on the last trading day of such futures contract (all pursuant to the rules of ICE Futures Europe), then the second nearby month futures contract for Brent crude oil, as made public by ICE Futures Europe and displayed on the Bloomberg Professional® service (“Bloomberg”) under the symbol “CO1” or “CO2,” as applicable, on that day |
| Pricing Date: |
July 1, 2022 |
| Original Issue Date: |
On or about July 7, 2022 (Settlement Date) |
| Observation Date†: |
July 26, 2023 |
| Maturity Date†: |
July 31, 2023 |
| CUSIP: |
48133DL32 |
| † | Subject to postponement in the event of certain market disruption events and as described under “General Terms of Notes —
Postponement of a Determination Date — Notes Linked to a Single Underlying — Notes Linked to a Single Commodity or Commodity
Futures Contract” and “General Terms of Notes — Postponement of a Payment Date” in the accompanying product supplement
or early acceleration in the event of a commodity hedging disruption event as described under “General Terms of Notes — Consequences
of a Commodity Hedging Disruption Event — Acceleration of the Notes” in the accompanying product supplement and in “Selected
Risk Considerations — Risks Relating to the Notes Generally — We May Accelerate Your Notes If a Commodity Hedging Disruption
Event Occurs” in this pricing supplement |
Investing in the notes involves a number of risks. See “Risk Factors”
beginning on page S-2 of the prospectus supplement, “Risk Factors” beginning on page PS-11 of the accompanying product supplement
and “Selected Risk Considerations” beginning on page PS-5 of this pricing supplement.
Neither the Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”)
nor any state securities commission has approved or disapproved of the notes or passed upon the accuracy or the adequacy of this pricing
supplement or the accompanying product supplement, prospectus supplement and prospectus. Any representation to the contrary is a criminal
offense.
| |
Price to Public (1) |
Fees and Commissions (2) |
Proceeds to Issuer |
| Per note |
$1,000 |
$10 |
$990 |
| Total |
$950,000 |
$9,500 |
$940,500 |
| (1) | See “Supplemental Use of Proceeds” in this pricing
supplement for information about the components of the price to public of the notes. |
| (2) | J.P. Morgan Securities LLC, which we refer to as JPMS, acting as agent for JPMorgan Financial,
will pay all of the selling commissions of $10.00 per $1,000 principal amount note it receives from us to other affiliated or unaffiliated
dealers. See “Plan of Distribution (Conflicts of Interest)” in the accompanying product supplement. |
The estimated value of the notes,
when the terms of the notes were set, was $944.60 per $1,000 principal amount note. See “The Estimated Value of the Notes”
in this pricing supplement for additional information.
The notes are not bank deposits, are not insured by the Federal Deposit
Insurance Corporation or any other governmental agency and are not obligations of, or guaranteed by, a bank.

Additional Terms Specific to the
Notes
You should read this pricing supplement together with the
accompanying prospectus, as supplemented by the accompanying prospectus supplement relating to our Series A medium-term notes, of which
these notes are a part, and the more detailed information contained in the accompanying product supplement. This pricing supplement,
together with the documents listed below, contains the terms of the notes and supersedes all other prior or contemporaneous oral statements
as well as any other written materials including preliminary or indicative pricing terms, correspondence, trade ideas, structures for
implementation, sample structures, fact sheets, brochures or other educational materials of ours. You should carefully consider, among
other things, the matters set forth in the “Risk Factors” section of the accompanying product supplement, as the notes involve
risks not associated with conventional debt securities. We urge you to consult your investment, legal, tax, accounting and other advisers
before you invest in the notes.
You may access these documents on the SEC website at www.sec.gov
as follows (or if such address has changed, by reviewing our filings for the relevant date on the SEC website):
Our Central Index Key, or CIK, on the SEC website is 1665650,
and JPMorgan Chase & Co.’s CIK is 19617. As used in this pricing supplement, “we,” “us” and “our”
refer to JPMorgan Financial.
Supplemental Terms of the Notes
For purposes of the notes offered by this pricing supplement:
(1) the consequences
of a commodity hedging disruption event are described under “General Terms of Notes — Consequences of a Commodity Hedging
Disruption Event — Acceleration of the Notes” in the accompanying product supplement; and
(2) the Observation
Date is a “Determination Date” as described in the accompanying product supplement and is subject to postponement as described
under “General Terms of Notes — Postponement of a Determination Date — Notes Linked to a Single Underlying — Notes
Linked to a Commodity or Commodity Futures Contract” in the accompanying product supplement.
The notes are not futures contracts or swaps and are not
regulated under the Commodity Exchange Act of 1936, as amended (the “Commodity Exchange Act”). The notes are offered pursuant
to an exemption from regulation under the Commodity Exchange Act, commonly known as the hybrid instrument exemption, that is available
to securities that have one or more payments indexed to the value, level or rate of one or more commodities, as set out in section 2(f)
of that statute. Accordingly, you are not afforded any protection provided by the Commodity Exchange Act or any regulation promulgated
by the Commodity Futures Trading Commission.
| | |
| JPMorgan Structured Investments — | PS-1 |
| Contingent Buffered Notes Linked to a Brent Crude Oil Futures Contract | |
What Is the Total Return on the
Notes at Maturity, Assuming a Range of Performances for the Commodity Futures Contract?
The following table and examples illustrate the hypothetical
total return and the hypothetical payment at maturity on the notes. The “total return” as used in this pricing supplement
is the number, expressed as a percentage, that results from comparing the payment at maturity per $1,000 principal amount note to $1,000.
Each hypothetical total return or payment at maturity set forth below assumes an Initial Contract Price of $100 and reflects the Contingent
Digital Return of 16.00% and the Contingent Buffer Percentage of 50%.
The hypothetical
Initial Contract Price of $100 has been chosen for illustrative purposes only and does not represent the actual Initial Contract Price.
The actual Initial Contract Price is the Contract Price on the Pricing Date and is specified under “Key Terms — Initial Contract
Price” in this pricing supplement. For historical data regarding the actual Contract Prices, please see the historical information
set forth under “Historical Information” in this pricing supplement.
Each hypothetical total return or payment at maturity
set forth below is for illustrative purposes only and may not be the actual total return or payment at maturity applicable to a purchaser
of the notes. The numbers appearing in the following table and in the examples below have been rounded for ease of analysis.
Ending
Contract
Price |
Contract
Return |
Total Return |
| $180.00 |
80.00% |
16.00% |
| $170.00 |
70.00% |
16.00% |
| $160.00 |
60.00% |
16.00% |
| $150.00 |
50.00% |
16.00% |
| $140.00 |
40.00% |
16.00% |
| $130.00 |
30.00% |
16.00% |
| $120.00 |
20.00% |
16.00% |
| $116.00 |
16.00% |
16.00% |
| $110.00 |
10.00% |
16.00% |
| $105.00 |
5.00% |
16.00% |
| $102.50 |
2.50% |
16.00% |
| $100.00 |
0.00% |
16.00% |
| $97.50 |
-2.50% |
16.00% |
| $95.00 |
-5.00% |
16.00% |
| $90.00 |
-10.00% |
16.00% |
| $80.00 |
-20.00% |
16.00% |
| $70.00 |
-30.00% |
16.00% |
| $60.00 |
-40.00% |
16.00% |
| $50.00 |
-50.00% |
16.00% |
| $49.99 |
-50.01% |
-50.01% |
| $40.00 |
-60.00% |
-60.00% |
| $30.00 |
-70.00% |
-70.00% |
| $20.00 |
-80.00% |
-80.00% |
| $10.00 |
-90.00% |
-90.00% |
| $0.00 |
-100.00% |
-100.00% |
| | |
| JPMorgan Structured Investments — | PS-2 |
| Contingent Buffered Notes Linked to a Brent Crude Oil Futures Contract | |
Hypothetical Examples of Amount
Payable at Maturity
The following examples illustrate how the payment at
maturity in different hypothetical scenarios is calculated.
Example 1: The price of the Commodity Futures Contract
increases from the Initial Contract Price of $100 to an Ending Contract Price of $105.
Because the Ending Contract Price of $105 is greater
than the Initial Contract Price of $100, regardless of the Contract Return, the investor receives a payment at maturity of $1,160.00 per
$1,000 principal amount note, calculated as follows:
$1,000 + ($1,000 × 16.00%)
= $1,160.00
Example 2: The price of the Commodity Futures Contract
decreases from the Initial Contract Price of $100 to an Ending Contract Price of $50.
Although the Contract Return is negative, because the
Ending Contract Price of $50 is less than the Initial Contract Price of $100 by up to the Contingent Buffer Percentage of 50%, the investor
receives a payment at maturity of $1,160.00 per $1,000 principal amount note, calculated as follows:
$1,000 + ($1,000 × 16.00%)
= $1,160.00
Example 3: The price of the Commodity Futures Contract
increases from the Initial Contract Price of $100 to an Ending Contract Price of $140.
Because the Ending Contract Price of $140 is greater
than the Initial Contract Price of $100 and although the Contract Return of 40% exceeds the Contingent Digital Return of 16.00%, the investor
is entitled to only the Contingent Digital Return and receives a payment at maturity of $1,160.00 per $1,000 principal amount note, calculated
as follows:
$1,000 + ($1,000 × 16.00%)
= $1,160.00
Example 4: The price of the Commodity Futures Contract
decreases from the Initial Contract Price of $100 to an Ending Contract Price of $40.
Because the Ending Contract Price of $40 is less than
the Initial Contract Price of $100 by more than the Contingent Buffer Percentage of 50% and the Contract Return is -60%, the investor
receives a payment at maturity of $400 per $1,000 principal amount note, calculated as follows:
$1,000 + ($1,000 × -60%) =
$400
The hypothetical returns and hypothetical payments on
the notes shown above apply only if you hold the notes for their entire term. These hypotheticals do not reflect fees or expenses
that would be associated with any sale in the secondary market. If these fees and expenses were included, the hypothetical returns and
hypothetical payments shown above would likely be lower.
| | |
| JPMorgan Structured Investments — | PS-3 |
| Contingent Buffered Notes Linked to a Brent Crude Oil Futures Contract | |
Selected Purchase Considerations
| · | FIXED APPRECIATION POTENTIAL — If the Ending
Index Level is greater than or equal to the Initial Index level or is less than the Initial Index Level by up to the Contingent Buffer
Percentage, you will receive a fixed return equal to the Contingent Digital Return of 16.00% at maturity, which also reflects the maximum
return on the notes at maturity. Because the notes are our unsecured and unsubordinated obligations, the payment of which is fully
and unconditionally guaranteed by JPMorgan Chase & Co., payment of any amount on the notes is subject to our ability to pay our obligations
as they become due and JPMorgan Chase & Co.’s ability to pay its obligations as they become due. |
| · | LIMITED PROTECTION AGAINST LOSS — We will pay
you at least your principal back at maturity if the Ending Contract Price is greater than or equal to the Initial Contract Price or is
less than the Initial Contract Price by up to the Contingent Buffer Percentage of 50%. If the Ending Contract Price is less than the Initial
Contract Price by more than the Contingent Buffer Percentage, for every 1% that the Ending Contract Price is less than the Initial Contract
Price, you will lose an amount equal to 1% of the principal amount of your notes. Under these circumstances, you will lose more than 50%
of your principal amount at maturity and may lose all of your principal amount at maturity. |
| · | RETURN LINKED TO A BRENT CRUDE OIL FUTURES CONTRACT —
The return on the notes is linked to the official
settlement price per barrel on ICE Futures Europe of the first nearby month (or, in some circumstances, in the second nearby month) futures
contract for Brent crude oil, stated in U.S. dollars as made public by ICE Futures Europe and displayed on the applicable Bloomberg page.
For additional information about the Commodity Futures Contract, see the information set forth under “The Underlyings — Commodity
Futures Contracts” in the accompanying product supplement. |
| · | TAX TREATMENT — You should review carefully
the section entitled “Material U.S. Federal Income Tax Consequences” in the accompanying product supplement no. 2-II.
The following discussion, when read in combination with that section, constitutes the full opinion of our special tax counsel, Davis Polk
& Wardwell LLP, regarding the material U.S. federal income tax consequences of owning and disposing of notes. |
Based on current market conditions, in the
opinion of our special tax counsel it is reasonable to treat the notes as “open transactions” that are not debt instruments
for U.S. federal income tax purposes, as more fully described in “Material U.S. Federal Income Tax Consequences — Tax Consequences
to U.S. Holders — Notes Treated as Open Transactions That Are Not Debt Instruments” in the accompanying product supplement.
Assuming this treatment is respected, the gain or loss on your notes should be treated as long-term capital gain or loss if you hold your
notes for more than a year, whether or not you are an initial purchaser of notes at the issue price. However, the IRS or a court
may not respect this treatment, in which case the timing and character of any income or loss on the notes could be materially and adversely
affected. In addition, in 2007 Treasury and the IRS released a notice requesting comments on the U.S. federal income tax treatment
of “prepaid forward contracts” and similar instruments. The notice focuses in particular on whether to require investors
in these instruments to accrue income over the term of their investment. It also asks for comments on a number of related topics,
including the character of income or loss with respect to these instruments; the relevance of factors such as the nature of the underlying
property to which the instruments are linked; the degree, if any, to which income (including any mandated accruals) realized by non-U.S.
investors should be subject to withholding tax; and whether these instruments are or should be subject to the “constructive ownership”
regime, which very generally can operate to recharacterize certain long-term capital gain as ordinary income and impose a notional interest
charge. While the notice requests comments on appropriate transition rules and effective dates, any Treasury regulations or other
guidance promulgated after consideration of these issues could materially and adversely affect the tax consequences of an investment in
the notes, possibly with retroactive effect. You should consult your tax adviser regarding the U.S. federal income tax consequences
of an investment in the notes, including possible alternative treatments and the issues presented by this notice.
| | |
| JPMorgan Structured Investments — | PS-4 |
| Contingent Buffered Notes Linked to a Brent Crude Oil Futures Contract | |
Selected Risk Considerations
An investment in the notes involves significant risks.
Investing in the notes is not equivalent to investing directly in the Commodity Futures Contract or in any exchange-traded or over-the-counter
instruments based on, or other instruments linked to, any of the foregoing. These risks are explained in more detail in the “Risk
Factors” sections of the accompanying prospectus supplement and the accompanying product supplement.
Risks Relating to the Notes Generally
| · | YOUR INVESTMENT IN THE
NOTES MAY RESULT IN A LOSS — The notes do not guarantee any return of principal. The return on the notes at maturity is dependent
on the performance of the Commodity Futures Contract and will depend on whether, and the extent to which, the Contract Return is positive
or negative. Your investment will be exposed to a loss if the Ending Contract Price is less than the Initial Contract Price by more than
the Contingent Buffer Percentage of 50%. In this case, for every 1% that the Ending Contract Price is less than the Initial Contract Price,
you will lose an amount equal to 1% of the principal amount of your notes. Under these circumstances, you will lose more than 50% of your
principal amount at maturity and may lose all of your principal amount at maturity. |
| · | YOUR MAXIMUM GAIN ON THE
NOTES IS LIMITED TO THE CONTINGENT DIGITAL RETURN — If the Ending Index Level is greater than or equal to the Initial Index
Level or is less than the Initial Index Level by up to the Contingent Buffer Percentage, for each $1,000 principal amount note, you will
receive at maturity $1,000 plus an additional return equal to the Contingent Digital Return, regardless of the appreciation in
the Index, which may be significant. |
| · | YOUR ABILITY TO RECEIVE
THE CONTINGENT DIGITAL RETURN MAY TERMINATE ON THE OBSERVATION DATE — If the Ending Contract Price is less than the Initial
Contract Price by more than the Contingent Buffer Percentage of 50%, you will not be entitled to receive the Contingent Digital Return
at maturity. Under these circumstances, you will lose more than 50% of your principal amount at maturity and may lose all of your principal
amount at maturity. |
| · | CREDIT RISKS OF JPMORGAN
FINANCIAL AND JPMORGAN CHASE & CO. — The notes are subject to our and JPMorgan Chase & Co.’s credit risks, and
our and JPMorgan Chase & Co.’s credit ratings and credit spreads may adversely affect the market value of the notes. Investors
are dependent on our and JPMorgan Chase & Co.’s ability to pay all amounts due on the notes. Any actual or potential change
in our or JPMorgan Chase & Co.’s creditworthiness or credit spreads, as determined by the market for taking that credit risk,
is likely to adversely affect the value of the notes. If we and JPMorgan Chase & Co. were to default on our payment obligations,
you may not receive any amounts owed to you under the notes and you could lose your entire investment. |
| · | AS A FINANCE SUBSIDIARY,
JPMORGAN FINANCIAL HAS NO INDEPENDENT OPERATIONS AND HAS LIMITED ASSETS — As a finance subsidiary of JPMorgan Chase & Co.,
we have no independent operations beyond the issuance and administration of our securities. Aside from the initial capital contribution
from JPMorgan Chase & Co., substantially all of our assets relate to obligations of our affiliates to make payments under loans made
by us or other intercompany agreements. As a result, we are dependent upon payments from our affiliates to meet our obligations under
the notes. If these affiliates do not make payments to us and we fail to make payments on the notes, you may have to seek payment under
the related guarantee by JPMorgan Chase & Co., and that guarantee will rank pari passu with all other unsecured and unsubordinated
obligations of JPMorgan Chase & Co. |
| · | THE BENEFIT PROVIDED BY THE CONTINGENT BUFFER PERCENTAGE
MAY TERMINATE ON THE OBSERVATION DATE — If the Ending Contract Price is less than the Initial Contract Price by more than the
Contingent Buffer Percentage, the benefit provided by the Contingent Buffer Percentage will terminate and you will be fully exposed to
any depreciation of the Commodity Futures Contract from the Initial Contract Price to the Ending Contract Price. |
| · | OWNING THE NOTES IS NOT THE SAME AS OWNING BRENT CRUDE
OIL FUTURES CONTRACTS — The return on your notes will not reflect the return you would realize if you actually purchased Brent
crude oil futures contracts or exchange-traded or over-the-counter instruments based on Brent crude oil futures contracts. You will not
have any rights that holders of such assets or instruments have. |
| · | WE MAY ACCELERATE YOUR NOTES IF A COMMODITY HEDGING DISRUPTION
EVENT OCCURS — If we or our affiliates are unable to effect transactions necessary to hedge our obligations under the notes
due to a commodity hedging disruption event, we may, in our sole and absolute discretion, accelerate the payment on your notes and pay
you an amount determined in good faith and in a commercially reasonable manner by the calculation agent. If the payment on your notes
is accelerated, your investment may result in a loss and you may not be able to reinvest your money in a comparable investment. Please
see “General Terms of Notes — Consequences of a Commodity Hedging Disruption Event — Acceleration of the Notes”
in the accompanying product supplement for more information. |
| · | NO INTEREST PAYMENTS — As a holder of the notes,
you will not receive any interest payments. |
| · | LACK OF LIQUIDITY — The notes will not be listed
on any securities exchange. JPMS intends to offer to purchase the notes in the secondary market but is not required to do so. Even if
there is a secondary market, it may not provide enough liquidity to allow you to trade or sell the notes easily. Because other dealers
are not likely to make a secondary market for the notes, the price at which you may be able to trade your notes is likely to depend on
the price, if any, at which JPMS is willing to buy the notes. |
Risks Relating
to Conflicts of Interest
| · | POTENTIAL CONFLICTS — We and our affiliates
play a variety of roles in connection with the issuance of the notes, including acting as calculation agent and as an agent of the offering
of the notes, hedging our obligations under the notes |
| | |
| JPMorgan Structured Investments — | PS-5 |
| Contingent Buffered Notes Linked to a Brent Crude Oil Futures Contract | |
and making the assumptions used to determine the pricing of
the notes and the estimated value of the notes when the terms of the notes are set, which we refer to as the estimated value of the notes.
In performing these duties, our and JPMorgan Chase & Co.’s economic interests and the economic interests of the calculation
agent and other affiliates of ours are potentially adverse to your interests as an investor in the notes. In addition, our and JPMorgan
Chase & Co.’s business activities, including hedging and trading activities, could cause our and JPMorgan Chase & Co.’s
economic interests to be adverse to yours and could adversely affect any payment on the notes and the value of the notes. It is possible
that hedging or trading activities of ours or our affiliates in connection with the notes could result in substantial returns for us or
our affiliates while the value of the notes declines. Please refer to “Risk Factors — Risks Relating to Conflicts of Interest”
in the accompanying product supplement for additional information about these risks.
Risks Relating
to the Estimated Value and Secondary Market Prices of the Notes
| · | THE ESTIMATED VALUE OF THE NOTES IS LOWER THAN THE ORIGINAL
ISSUE PRICE (PRICE TO PUBLIC) OF THE NOTES — The estimated value of the notes is only an estimate determined by reference to
several factors. The original issue price of the notes exceeds the estimated value of the notes because costs associated with selling,
structuring and hedging the notes are included in the original issue price of the notes. These costs include the selling commissions,
the projected profits, if any, that our affiliates expect to realize for assuming risks inherent in hedging our obligations under the
notes and the estimated cost of hedging our obligations under the notes. See “The Estimated Value of the Notes” in this pricing
supplement. |
| · | THE ESTIMATED VALUE OF THE NOTES DOES NOT REPRESENT FUTURE
VALUES OF THE NOTES AND MAY DIFFER FROM OTHERS’ ESTIMATES — The estimated value of the notes is determined by reference
to internal pricing models of our affiliates when the terms of the notes are set. This estimated value of the notes is based on market
conditions and other relevant factors existing at that time and assumptions about market parameters, which can include volatility, interest
rates and other factors. Different pricing models and assumptions could provide valuations for the notes that are greater than or less
than the estimated value of the notes. In addition, market conditions and other relevant factors in the future may change, and any assumptions
may prove to be incorrect. On future dates, the value of the notes could change significantly based on, among other things, changes in
market conditions, our or JPMorgan Chase & Co.’s creditworthiness, interest rate movements and other relevant factors, which
may impact the price, if any, at which JPMS would be willing to buy notes from you in secondary market transactions. See “The Estimated
Value of the Notes” in this pricing supplement. |
| · | THE ESTIMATED VALUE OF THE NOTES IS DERIVED BY REFERENCE
TO AN INTERNAL FUNDING RATE — The internal funding rate used in the determination of the estimated value of the notes is based
on, among other things, our and our affiliates’ view of the funding value of the notes as well as the higher issuance, operational
and ongoing liability management costs of the notes in comparison to those costs for the conventional fixed-rate debt of JPMorgan Chase
& Co. The use of an internal funding rate and any potential changes to that rate may have an adverse effect on the terms of the notes
and any secondary market prices of the notes. See “The Estimated Value of the Notes” in this pricing supplement. |
| · | THE VALUE OF THE NOTES AS PUBLISHED BY JPMS (AND WHICH
MAY BE REFLECTED ON CUSTOMER ACCOUNT STATEMENTS) MAY BE HIGHER THAN THE THEN-CURRENT ESTIMATED VALUE OF THE NOTES FOR A LIMITED TIME PERIOD
— We generally expect that some of the costs included in the original issue price of the notes will be partially paid back to you
in connection with any repurchases of your notes by JPMS in an amount that will decline to zero over an initial predetermined period.
These costs can include projected hedging profits, if any, and, in some circumstances, estimated hedging costs and our internal secondary
market funding rates for structured debt issuances. See “Secondary Market Prices of the Notes” in this pricing supplement
for additional information relating to this initial period. Accordingly, the estimated value of your notes during this initial period
may be lower than the value of the notes as published by JPMS (and which may be shown on your customer account statements). |
| · | SECONDARY MARKET PRICES OF THE NOTES WILL LIKELY BE LOWER
THAN THE ORIGINAL ISSUE PRICE OF THE NOTES — Any secondary market prices of the notes will likely be lower than the original
issue price of the notes because, among other things, secondary market prices take into account our internal secondary market funding
rates for structured debt issuances and, also, because secondary market prices (a) exclude selling commissions and (b) may exclude projected
hedging profits, if any, and estimated hedging costs that are included in the original issue price of the notes. As a result, the price,
if any, at which JPMS will be willing to buy notes from you in secondary market transactions, if at all, is likely to be lower than the
original issue price. Any sale by you prior to the Maturity Date could result in a substantial loss to you. See the immediately following
risk consideration for information about additional factors that will impact any secondary market prices of the notes. |
The notes are not designed to be short-term
trading instruments. Accordingly, you should be able and willing to hold your notes to maturity. See “— Lack of Liquidity”
below.
| · | SECONDARY MARKET PRICES OF THE NOTES WILL BE IMPACTED
BY MANY ECONOMIC AND MARKET FACTORS — The secondary market price of the notes during their term will be impacted by a number
of economic and market factors, which may either offset or magnify each other, aside from the selling commissions, projected hedging profits,
if any, estimated hedging costs and the Contract Price, including: |
| · | any actual or potential change in our or JPMorgan Chase
& Co.’s creditworthiness or credit spreads; |
| · | customary bid-ask spreads for similarly sized trades; |
| · | our internal secondary market funding rates for structured
debt issuances; |
| · | the actual and expected volatility in the Contract Price
of the Commodity Futures Contract; |
| · | the time to maturity of the notes; |
| · | supply and demand trends for Brent crude oil or the exchange-traded
futures contracts on that commodity; |
| | |
| JPMorgan Structured Investments — | PS-6 |
| Contingent Buffered Notes Linked to a Brent Crude Oil Futures Contract | |
| · | interest and yield rates in the market generally; and |
| · | a variety of other economic, financial, political, regulatory,
geographical, agricultural, meteorological and judicial events. |
| · | Additionally, independent pricing vendors and/or third party
broker-dealers may publish a price for the notes, which may also be reflected on customer account statements. This price may be different
(higher or lower) than the price of the notes, if any, at which JPMS may be willing to purchase your notes in the secondary market. |
Risks Relating
to the Commodity Futures Contract
| · | COMMODITY FUTURES CONTRACTS ARE SUBJECT TO UNCERTAIN
LEGAL AND REGULATORY REGIMES — Commodity
futures contracts are subject to legal and regulatory regimes that may change in ways that could adversely affect our ability to hedge
our obligations under the notes and affect the price of the Commodity Futures Contract. Any future regulatory changes may have a
substantial adverse effect on the value of your notes. Additionally, in October 2020, the U.S. Commodity Futures Trading Commission
adopted rules to establish revised or new position limits on 25 agricultural, metals and energy commodity derivatives contracts.
The limits would apply to a person’s combined position in the specified 25 futures contracts and options on futures (“core
referenced futures contracts”), futures and options on futures directly or indirectly linked to the core referenced futures contracts,
and economically equivalent swaps. These rules came into effect on January 1, 2022 for covered futures and options on futures contracts
and will come into effect on January 1, 2023 for covered swaps. The rules may reduce liquidity in the exchange-traded market for
those commodity-based futures contracts, which may, in turn, have an adverse effect on any payments on the notes. Furthermore, we
or our affiliates may be unable as a result of those restrictions to effect transactions necessary to hedge our obligations under the
notes resulting in a commodity hedging disruption event, in which case we may, in our sole and absolute discretion, accelerate the payment
on your notes. See “— Risks Relating to the Notes Generally — We May Accelerate Your Notes If a Commodity Hedging
Disruption Event Occurs” above. |
| · | PRICES OF COMMODITY FUTURES CONTRACTS ARE CHARACTERIZED
BY HIGH AND UNPREDICTABLE VOLATILITY — Market prices of commodity futures contracts tend to be highly volatile and may fluctuate
rapidly based on numerous factors, including the factors that affect the price of the commodity underlying the Commodity Futures Contract.
See “— The Market Price of Brent Crude Oil Will Affect the Value of the Notes” below. The Contract Price is subject
to variables that may be less significant to the values of traditional securities, such as stocks and bonds. These variables may create
additional investment risks that cause the value of the notes to be more volatile than the values of traditional securities. As a general
matter, the risk of low liquidity or volatile pricing around the maturity date of a commodity futures contract is greater than in the
case of other futures contracts because (among other factors) a number of market participants take physical delivery of the underlying
commodities. Many commodities are also highly cyclical. The high volatility and cyclical nature of commodity markets may render such an
investment inappropriate as the focus of an investment portfolio. |
| · | THE MARKET PRICE OF BRENT CRUDE OIL WILL AFFECT THE VALUE
OF THE NOTES — Because the notes are linked to the performance of the Contract Price of the Commodity Futures Contract, we expect
that generally the market value of the notes will depend in part on the market price of Brent crude oil. The price of Brent crude oil
is primarily affected by the global demand for and supply of crude oil, but is also influenced significantly from time to time by speculative
actions and by currency exchange rates. Crude oil prices are volatile and subject to dislocation. Demand for refined petroleum products
by consumers, as well as the agricultural, manufacturing and transportation industries, affects the price of crude oil. Crude oil’s
end-use as a refined product is often as transport fuel, industrial fuel and in-home heating fuel. Potential for substitution in most
areas exists, although considerations, including relative cost, often limit substitution levels. Because the precursors of demand for
petroleum products are linked to economic activity, demand will tend to reflect economic conditions. Demand is also influenced by government
regulations, such as environmental or consumption policies. In addition to general economic activity and demand, prices for crude oil
are affected by political events, labor activity and, in particular, direct government intervention (such as embargos) or supply disruptions
in major oil producing regions of the world. These events tend to affect oil prices worldwide, regardless of the location of the event.
Supply for crude oil may increase or decrease depending on many factors. These include production decisions by the Organization of the
Petroleum Exporting Countries (“OPEC”) and other crude oil producers. Crude oil prices are determined with significant influence
by OPEC. OPEC has the potential to influence oil prices worldwide because its members possess a significant portion of the world’s
oil supply. In the event of sudden disruptions in the supplies of oil, such as those caused by war, natural events, accidents or acts
of terrorism, prices of oil futures contracts could become extremely volatile and unpredictable. Also, sudden and dramatic changes in
the futures market may occur, for example, upon a cessation of hostilities that may exist in countries producing oil, the introduction
of new or previously withheld supplies into the market or the introduction of substitute products or commodities. Crude oil prices may
also be affected by short-term changes in supply and demand because of trading activities in the oil market and seasonality (e.g.,
weather conditions such as hurricanes). It is not possible to predict the aggregate effect of all or any combination of these factors. |
| · | Futures Contracts on Brent
Crude Oil are the Benchmark Crude Oil Contracts in European and Asian Markets and May Be Affected by Economic Conditions in Europe and
Asia — Because futures contracts on Brent crude
oil are the benchmark crude oil contracts in European and Asian markets, the Commodity Futures Contract will be affected by economic conditions
in Europe and Asia. A decline in economic activity in Europe or Asia could result in decreased demand for crude oil and for futures contracts
on crude oil, which could adversely affect the price of the Commodity Futures Contract and, therefore, the notes. |
| | |
| JPMorgan Structured Investments — | PS-7 |
| Contingent Buffered Notes Linked to a Brent Crude Oil Futures Contract | |
| · | There Are Risks Relating to
the Contract Price Being Determined by ICE Futures Europe —
Futures contracts on Brent crude oil are traded on ICE Futures Europe. The Contract Price will be determined by reference to the official
settlement price per barrel on ICE Futures Europe of the first nearby month futures contract for Brent crude oil (or, in some circumstances,
the second nearby month futures contract for Brent crude oil), stated in U.S. dollars, as made public by ICE Futures Europe and displayed
on the applicable Bloomberg page. Investments in notes linked to the value of commodity futures contracts that are traded on non-U.S.
exchanges, such as ICE Futures Europe, involve risks associated with the markets in those countries, including risks of volatility in
those markets and governmental intervention in those markets. |
| · | A DECISION BY ICE FUTURES EUROPE TO INCREASE MARGIN REQUIREMENTS
FOR BRENT CRUDE OIL FUTURES CONTRACTS MAY AFFECT THE CONTRACT PRICE — If ICE Futures Europe increases the amount of collateral
required to be posted to hold positions in the futures contracts on Brent crude oil (i.e., the margin requirements), market participants
who are unwilling or unable to post additional collateral may liquidate their positions, which may cause the Contract Price to decline
significantly. |
| · | THE NOTES DO NOT OFFER DIRECT EXPOSURE TO COMMODITY SPOT
PRICES — The Commodity Futures Contract reflects the price of a futures contract, not a physical commodity (or its spot price).
The price of a futures contract reflects the expected value of the commodity upon delivery in the future, whereas the spot price of a
commodity reflects the immediate delivery value of the commodity. A variety of factors can lead to a disparity between the expected future
price of a commodity and the spot price at a given point in time, such as the cost of storing the commodity for the term of the futures
contract, interest charges incurred to finance the purchase of the commodity and expectations concerning supply and demand for the commodity.
The price movements of a futures contract are typically correlated with the movements of the spot price of the referenced commodity, but
the correlation is generally imperfect and price movements in the spot market may not be reflected in the futures market (and vice versa).
Accordingly, the notes may underperform a similar investment that is linked only to commodity spot prices. |
| · | SINGLE COMMODITY FUTURES CONTRACT PRICES TEND TO BE MORE
VOLATILE THAN, AND MAY NOT CORRELATE WITH, THE PRICES OF COMMODITIES GENERALLY — The notes are not linked to a diverse basket
of commodities, commodity futures contracts or a broad-based commodity index. The prices of the Commodity Futures Contract may not correlate
to the price of commodities or commodity futures contracts generally and may diverge significantly from the prices of commodities or commodity
futures contracts generally. Because the notes are linked a single commodity futures contract, they carry greater risk and may be more
volatile than notes linked to the prices of multiple commodities or commodity futures contracts or a broad-based commodity index. |
| · | SUSPENSION OR DISRUPTIONS OF MARKET TRADING IN THE COMMODITY
MARKETS AND RELATED FUTURES MARKETS MAY ADVERSELY AFFECT THE CONTRACT PRICE, AND THEREFORE THE VALUE OF THE NOTES — The commodity
markets are subject to temporary distortions or other disruptions due to various factors, including the lack of liquidity in the markets,
the participation of speculators and government regulation and intervention. In addition, U.S. futures exchanges and some foreign exchanges
have regulations that limit the amount of fluctuation in futures contract prices that may occur during a single day. These limits are
generally referred to as “daily price fluctuation limits” and the maximum or minimum price of a contract on any given day
as a result of these limits is referred to as a “limit price.” Once the limit price has been reached in a particular contract,
no trades may be made at a different price. Limit prices have the effect of precluding trading in a particular contract or forcing the
liquidation of contracts at disadvantageous times or prices. These circumstances could adversely affect the Contract Price of the Commodity
Futures Contract and, therefore, the value of your notes. |
| | |
| JPMorgan Structured Investments — | PS-8 |
| Contingent Buffered Notes Linked to a Brent Crude Oil Futures Contract | |
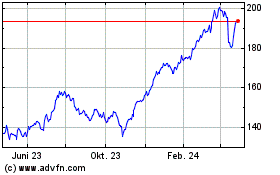
Historical Information
The following graph sets forth the historical performance
of the Commodity Futures Contract based on the weekly historical Contract Prices of the Commodity Futures Contract from January 6, 2017
through July 1, 2022. The Contract Price of the Commodity Futures Contract on July 1, 2022 was $111.63. We obtained the Contract Prices
of the Commodity Futures Contract above and below from the Bloomberg Professional® service (“Bloomberg”), without
independent verification.
The historical Contract Prices should not be taken as
an indication of future performance, and no assurance can be given as to the Contract Price on the Observation Date. There can be no assurance
that the performance of the Commodity Futures Contract will result in the return of any of your principal amount.

The Estimated Value of the Notes
The estimated value of the notes set forth on the cover
of this pricing supplement is equal to the sum of the values of the following hypothetical components: (1) a fixed-income debt component
with the same maturity as the notes, valued using the internal funding rate described below, and (2) the derivative or derivatives underlying
the economic terms of the notes. The estimated value of the notes does not represent a minimum price at which JPMS would be willing to
buy your notes in any secondary market (if any exists) at any time. The internal funding rate used in the determination of the estimated
value of the notes is based on, among other things, our and our affiliates’ view of the funding value of the notes as well as the
higher issuance, operational and ongoing liability management costs of the notes in comparison to those costs for the conventional fixed-rate
debt of JPMorgan Chase & Co. For additional information, see “Selected Risk Considerations — Risks Relating to the
Estimated Value and Secondary Market Prices of the Notes — The Estimated Value of the Notes Is Derived by Reference to an Internal
Funding Rate” in this pricing supplement. The value of the derivative or derivatives underlying the economic terms of the notes
is derived from internal pricing models of our affiliates. These models are dependent on inputs such as the traded market prices of comparable
derivative instruments and on various other inputs, some of which are market-observable, and which can include volatility, interest rates
and other factors, as well as assumptions about future market events and/or environments. Accordingly, the estimated value of the notes
is determined when the terms of the notes are set based on market conditions and other relevant factors and assumptions existing at that
time. See “Selected Risk Considerations — Risks Relating to the Estimated Value and Secondary Market Prices of the Notes —
The Estimated Value of the Notes Does Not Represent Future Values of the Notes and May Differ from Others’ Estimates” in this
pricing supplement.
The estimated value of the notes is lower than the original
issue price of the notes because costs associated with selling, structuring and hedging the notes are included in the original issue price
of the notes. These costs include the selling commissions paid to JPMS and other affiliated or unaffiliated dealers, the projected profits,
if any, that our affiliates expect to realize for assuming risks inherent in hedging our obligations under the notes and the estimated
cost of hedging our obligations under the notes. Because hedging our obligations entails risk and may be influenced by market forces beyond
our control, this hedging may result in a profit that is more or less than expected, or it may result in a loss. We or one or more of
our affiliates will retain any profits realized in hedging our obligations under the notes. See “Selected Risk Considerations —
Risks Relating to the Estimated Value and Secondary Market Prices of the Notes — The Estimated Value of the Notes Is Lower Than
the Original Issue Price (Price to Public) of the Notes” in this pricing supplement.
| | |
| JPMorgan Structured Investments — | PS-9 |
| Contingent Buffered Notes Linked to a Brent Crude Oil Futures Contract | |
Secondary Market Prices of the Notes
For information about factors that will impact any secondary
market prices of the notes, see “Selected Risk Considerations — Risks Relating to the Estimated Value and Secondary Market
Prices of the Notes — Secondary Market Prices of the Notes Will Be Impacted by Many Economic and Market Factors” in this pricing
supplement. In addition, we generally expect that some of the costs included in the original issue price of the notes will be partially
paid back to you in connection with any repurchases of your notes by JPMS in an amount that will decline to zero over an initial predetermined
period that is intended to be the shorter of six months and one-half of the stated term of the notes. The length of any such initial period
reflects the structure of the notes, whether our affiliates expect to earn a profit in connection with our hedging activities, the estimated
costs of hedging the notes and when these costs are incurred, as determined by our affiliates. See “Selected Risk Considerations
— Risks Relating to the Estimated Value and Secondary Market Prices of the Notes — The Value of the Notes as Published by
JPMS (and Which May Be Reflected on Customer Account Statements) May Be Higher Than the Then-Current Estimated Value of the Notes for
a Limited Time Period.”
Supplemental Use of Proceeds
The notes are offered to meet investor demand for products
that reflect the risk-return profile and market exposure provided by the notes. See “What Is the Total Return on the Notes at Maturity,
Assuming a Range of Performances for the Commodity Futures Contract?” and “Hypothetical Examples of Amounts Payable at Maturity”
in this pricing supplement for an illustration of the risk-return profile of the notes and “Selected Purchase Considerations —
Return Linked to a Brent Crude Oil Futures Contract” in this pricing supplement for a description of the market exposure provided
by the notes.
The original issue price of the notes is equal to the estimated
value of the notes plus the selling commissions paid to JPMS and other affiliated or unaffiliated dealers, plus (minus) the projected
profits (losses) that our affiliates expect to realize for assuming risks inherent in hedging our obligations under the notes, plus the
estimated cost of hedging our obligations under the notes.
Supplemental Plan of Distribution
We expect that delivery of the notes will be made against
payment for the notes on or about the Original Issue Date set forth on the front cover of this pricing supplement, which will be the third
business day following the Pricing Date of the notes (this settlement cycle being referred to as “T+3”). Under Rule 15c6-1
of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, trades in the secondary market generally are required to settle in two business days,
unless the parties to that trade expressly agree otherwise. Accordingly, purchasers who wish to trade notes on any date prior to two business
days before delivery will be required to specify an alternate settlement cycle at the time of any such trade to prevent a failed settlement
and should consult their own advisors.
Supplemental Information About the
Form of the Notes
The notes will initially be represented by a type of global
security that we refer to as a master note. A master note represents multiple securities that may be issued at different times and
that may have different terms. The trustee and/or paying agent will, in accordance with instructions from us, make appropriate entries
or notations in its records relating to the master note representing the notes to indicate that the master note evidences the notes.
Validity of the Notes and the Guarantee
In the opinion of Davis Polk & Wardwell LLP, as special
products counsel to JPMorgan Financial and JPMorgan Chase & Co., when the notes offered by this pricing supplement have been issued
by JPMorgan Financial pursuant to the indenture, the trustee and/or paying agent has made, in accordance with the instructions from JPMorgan
Financial, the appropriate entries or notations in its records relating to the master global note that represents such notes (the “master
note”), and such notes have been delivered against payment as contemplated herein, such notes will be valid and binding obligations
of JPMorgan Financial and the related guarantee will constitute a valid and binding obligation of JPMorgan Chase & Co., enforceable
in accordance with their terms, subject to applicable bankruptcy, insolvency and similar laws affecting creditors’ rights generally,
concepts of reasonableness and equitable principles of general applicability (including, without limitation, concepts of good faith, fair
dealing and the lack of bad faith), provided that such counsel expresses no opinion as to (i) the effect of fraudulent conveyance,
fraudulent transfer or similar provision of applicable law on the conclusions expressed above or (ii) any provision of the indenture that
purports to avoid the effect of fraudulent conveyance, fraudulent transfer or similar provision of applicable law by limiting the amount
of JPMorgan Chase & Co.’s obligation under the related guarantee. This opinion is given as of the date hereof and is limited
to the laws of the State of New York, the General Corporation Law of the State of Delaware and the Delaware Limited Liability Company
Act. In addition, this opinion is subject to customary assumptions about the trustee’s authorization, execution and delivery
of the indenture and its authentication of the master note and the validity, binding nature and enforceability of the indenture with respect
to the trustee, all as stated in the letter of such counsel dated May 6, 2022, which was filed as an exhibit to a Current Report on Form
8-K by JPMorgan Chase & Co. on May 6, 2022.
| | |
| JPMorgan Structured Investments — | PS-10 |
| Contingent Buffered Notes Linked to a Brent Crude Oil Futures Contract | |
JP Morgan Chase (NYSE:JPM)
Historical Stock Chart
Von Mär 2024 bis Apr 2024
JP Morgan Chase (NYSE:JPM)
Historical Stock Chart
Von Apr 2023 bis Apr 2024